Application of Low-E Glass in energy-efficient windows
Low-E Glass has become a key material for saving energy in today’s construction industry. What makes this type of glass unique is its ability to reflect heat effectively while allowing light through it too, thus making it particularly suitable for use in energy-saving windows.
What is Low-E Glass?
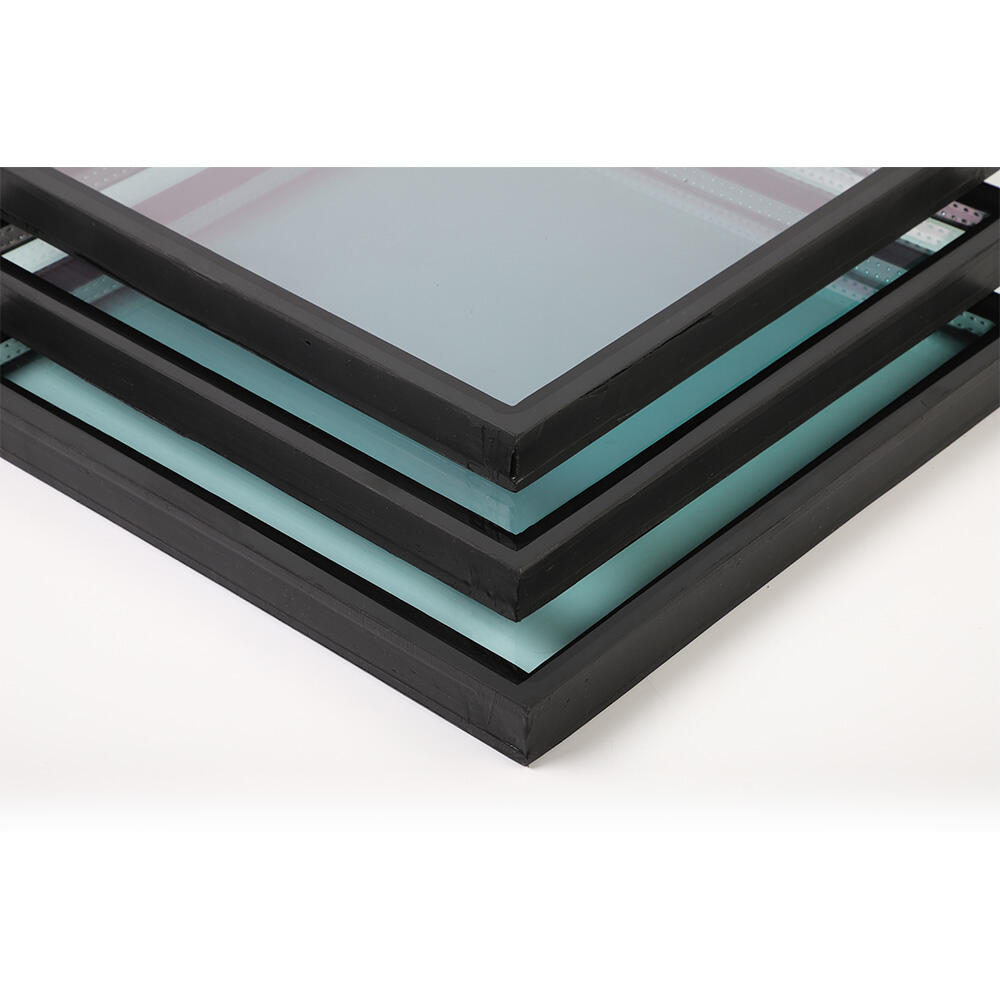
Low-E Glass is a kind of special glass which has been coated with a thin layer made from metal or metal oxides that reflects infrared radiation and decreases thermal conductivity while still letting visible lights pass through so as to achieve good lighting effects required by architectural works especially those aimed at conserving power such as insulated glazing units(IGUs).
Applications Of Low-E Glass In Energy Saving Windows
The use of Low-E Glass within energy-saving windows can be seen in the subsequent areas:
Increased Thermal Efficiency
One way in which Low-E Glass work is by reflecting back indoor warmth towards its source thus preventing it from escaping outside during winter seasons when people need them more than ever before; also, they act as a barrier against heat gain into rooms from external environment during summer days thus reducing reliance upon air conditioners. Therefore, using low emissivity coatings on window panes constitutes an important element towards achieving overall efficiency gains within structures.
Enhanced Lighting Efficiency
While being able to repel heat, most visible lights are allowed to go through them hence even if you close your eyes completely with blinds down you will still have enough natural light inside the house because sun rays can reach Low-E Glass directly without any interruption caused by different objects along their path such as trees or buildings. This implies that this feature significantly contributes not only to better quality illumination indoors but also reduces reliance upon artificial sources like bulbs leading to savings on electricity bills.
Minimization Of UV Damage
Majority ultraviolet rays are hindered by these materials which safeguard occupants’ health and safety vis-à-vis furniture fading plus other interior components’ degradation resulting from exposure to them over time. For instance, too much sun can cause cancer while causing colors of textiles used for upholstery purposes (carpets) fade away quickly after being installed next to windows where such kind of radiation prevails most frequently hence necessitating their replacement often otherwise they become unsightly due to loss in pigmentation thereby decreasing overall appeal.
Strengthening Window’s Durability
Low-E Glass possesses better resistance against adverse weather conditions and longer lifespan due to its special design as well as constituent materials employed during manufacturing process thus capable of withstanding various outdoor settings without undergoing significant deterioration like regular glasses would do under similar circumstances; this suggests that using low emissivities on window panes could lead to reduced maintenance needs along with associated costs arising from replacing worn out ones repeatedly over time.
Conclusion
The use of Low-E Glass in energy-efficient windows provides us with an effective way of saving power. We can improve the thermal efficiency not only by closing doors but also through installing such types of materials because they allow natural light into our houses even when closed thus reducing dependency on artificial lighting systems which consume much electricity. Additionally, low-E coatings increase occupant comfort levels within buildings especially during hot seasons since it reflects back most UV rays responsible for skin cancer development while at the same time preventing color fading caused by excessive exposure thereof among many others. Therefore, there is no doubt that Low-E Glass will play a more significant role in future construction industry activities.
Recommended Products
Hot News
-
The Amazing Properties and Uses of Glass
2024-01-10
-
Production raw materials and processes of glass products
2024-01-10
-
Co-create the future! A delegation from Atlantic El Tope Hotel visited our company
2024-01-10
-
ZRGlas Shines at Sydney Build EXPO 2024, Innovative Products Spark High Interest Among Clients
2024-05-06
-
How Low-E Glass Can Cut Energy Costs and Boost Insulation
2024-09-18

 EN
EN
 AR
AR
 CS
CS
 DA
DA
 NL
NL
 FI
FI
 FR
FR
 DE
DE
 EL
EL
 IT
IT
 JA
JA
 KO
KO
 PL
PL
 PT
PT
 RU
RU
 ES
ES
 TL
TL
 IW
IW
 ID
ID
 SR
SR
 SL
SL
 UK
UK
 VI
VI
 HU
HU
 TH
TH
 TR
TR
 FA
FA
 AF
AF
 MS
MS
 UR
UR
 HA
HA
 LO
LO
 LA
LA
 MI
MI
 MN
MN
 TA
TA
 TE
TE
 MY
MY
 SI
SI